Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) are two types of procedures use to treat depression. While both have proven to be effective in their treatment, there are significant differences in how these two procedures function.
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Originally introduced in the 1930s, ECT has come a long way in terms of effectiveness and safety as a medical procedure.
Mental conditions in which ECT has been successful in treating include catatonia as well as severe and treatment-resistant mood disorders. ECT has also been used as a last resort for treating obsessive-compulsive disorder, Parkinson's disease and Tourette syndrome among others.
You can also consult a therapist for tms therapy in Westbury.
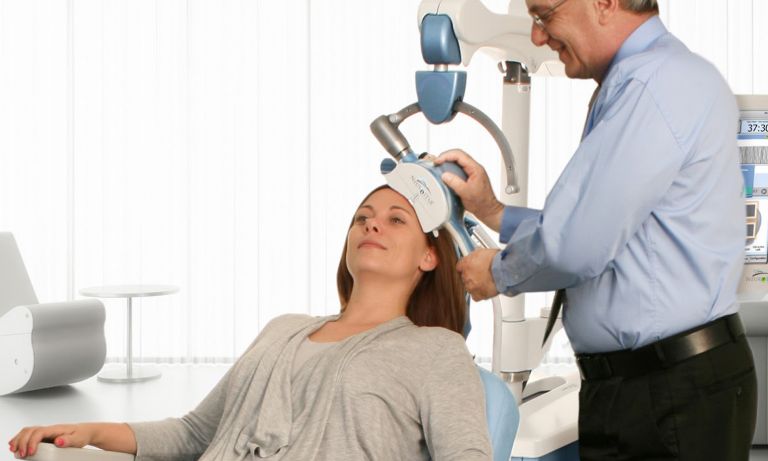
Image Source: Google
ECT treatment is administered in a controlled setting using electric currents that pass through a patient's brain, deliberately triggering a seizure in the process.
The seizure provokes changes in the brain physiology that appear to be successful in reversing the symptoms of mental illness in some patients. Researchers have yet to come to an agreeable conclusion on how the chemical changes evoked by ECT Therapy are able to successfully reduce these symptoms.
ECT sessions run between 20 to 30 minutes and are typically given two or three times weekly over a two to four week period. Patients tend to see results after two or three ECT treatments.
Risks associated with ECT treatment have decreased significantly from the time in which the procedure was practiced without a strict protocol in place.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
TMS therapy is conducted through the use of a treatment coil placed lightly against the scalp of patients sitting in a reclining chair. The coil emits magnetic fields that stimulate nerve cell activity in a brain area implicated regulating mood.
TMS Patients typically receive five weekly treatments over a six week period. Patients remain fully awake during a TMS therapy session, which lasts roughly 40 minutes.
Unlike ECT treatment, TMS therapy doesn't require anesthesia or possible hospital recovery time. While scalp pain is the most common side effect, rare incidences of seizures have also been reported during TMS treatment.
